Syringomyelia Vs Central Cord Syndrome
Syringomyelia vs central cord syndrome. Because it is a clinical diagnosis it is important for the emergency physician to consider this entity during their assessment particularly in trauma patients where this may be overlooked. Syringomyelia is cavitary expansion of central canal of spinal cord which gives rise to central cord syndrome. The first abnormality recognized may be a painless burn or cut.
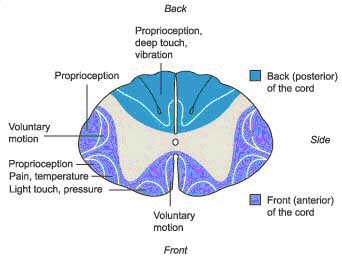
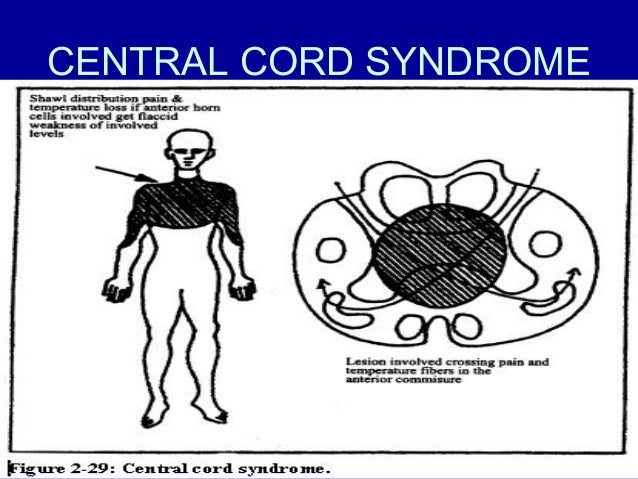
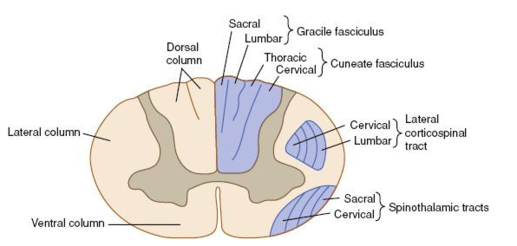
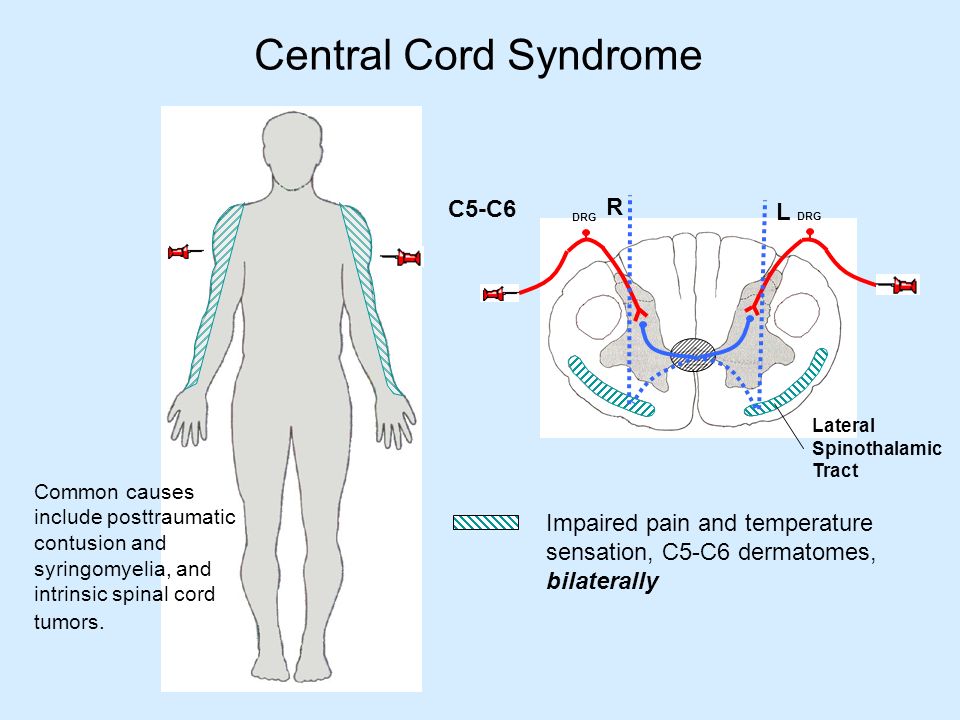
Common in the elderly with preexisting degenerative changes in the cervical spine. Injury to the central region of the spinal cord central corticospinal tracts and decussating fibers of the lateral spinothalamic tract Epidemiology. Syringomyelia located in the lumbosacral cord is likely derived from the same types of pathogenesis.
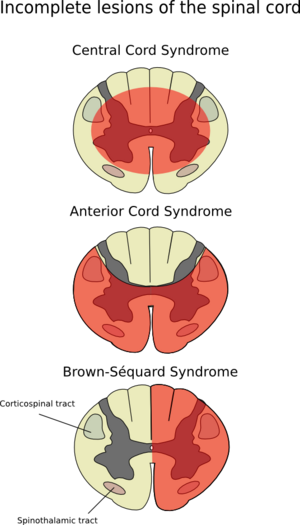
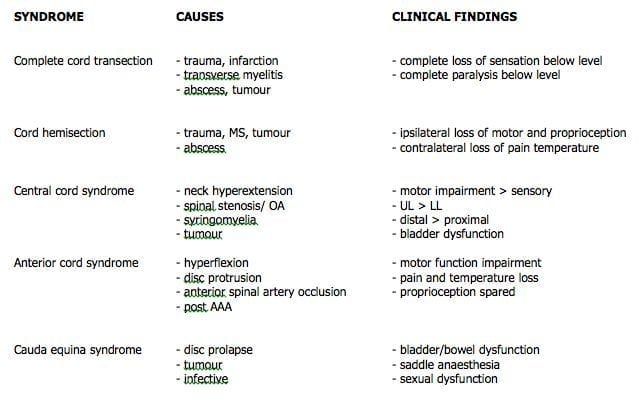
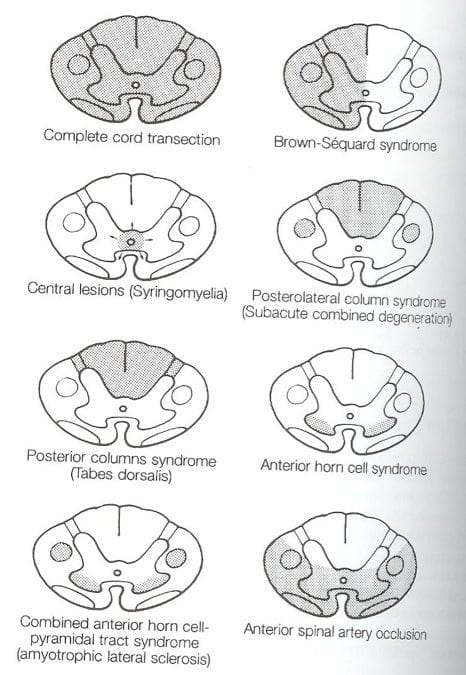
Most common location is lower cervical upper thorasic cord. The latter category includes those caused by 1 contusion 2 compression 3 traction 4 arachnoiditis 5 tumors and 6 ischemia. Syringomyelia develops in the center of the spinal cord causing a central cord syndrome see table Spinal Cord Syndromes.
So central cord syndrome is a cause of syringomyelia or. When cervical spinal cord is involved the patients may present with upper motor neuron weakness with preferential involvement of upper extremities man-in-the-barrel syndrome bladder dysfunction and variable sensory loss. Some physicians use the terms syringomyelia or hydromyelia interchangeably.
Some individuals have a condition related to syringomyelia known as hydrosyringomyelia which is characterized by abnormal widening of the central canal of the spinal cord the normal small canal running through the center of the spinal cord. Central cord syndrome can often be missed in the ED as the imaging in these patients is often unremarkable and their sensory deficits can be patchy. Most common type of incomplete cord syndrome.
Central Cord Syndrome Central cord syndrome may be caused by syringomyelia or intramedullary cord tumors. What are symptoms of syringomyelia. Most common cause of syringomyelia is chiari malformation.
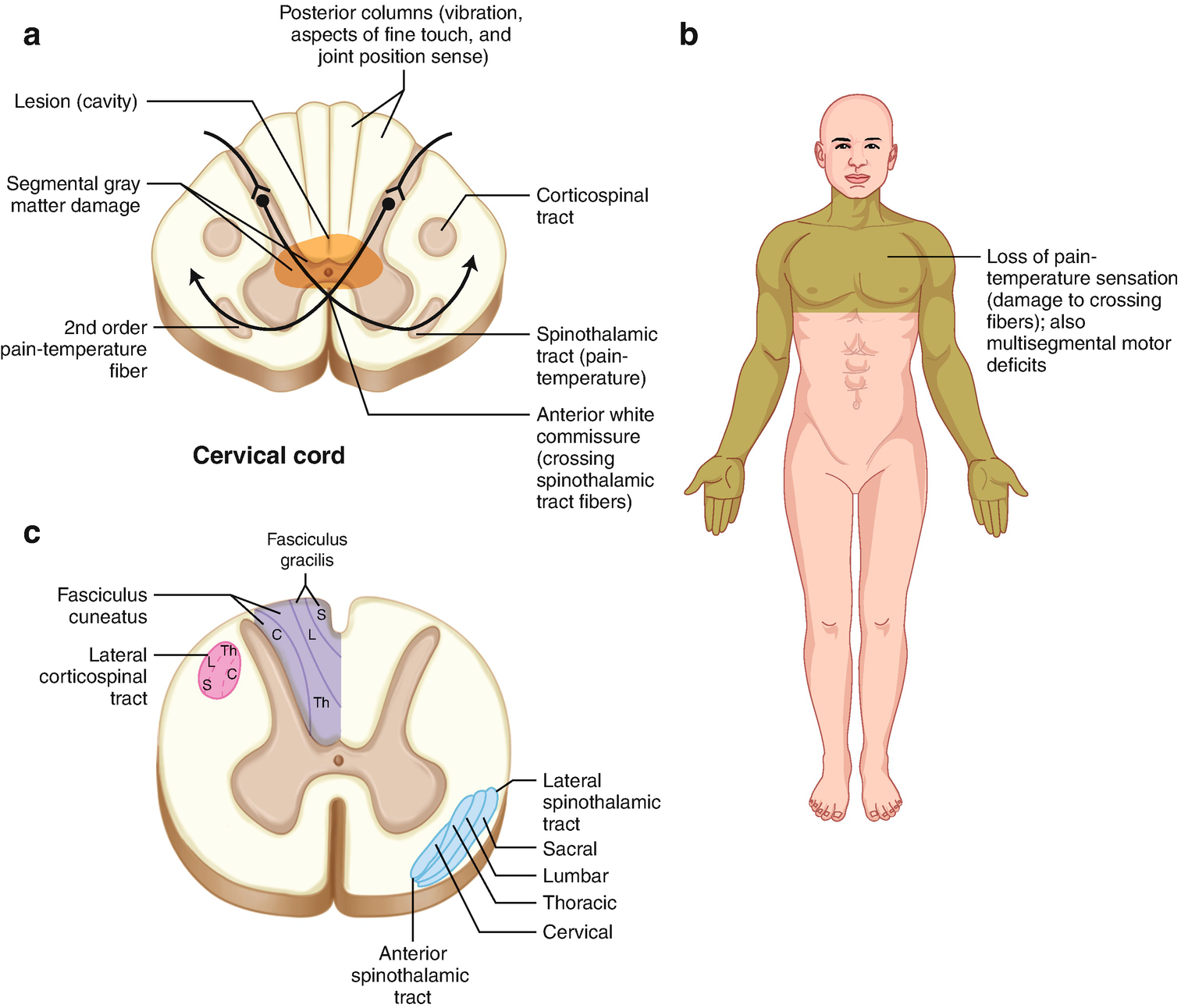
In syringomyelia the watery liquid known as cerebrospinal fluid CSFwhich normally surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cordbuilds up within the tissue of the spinal cord expands the central canal and forms a syrinx. Central cord syndrome doesnot equate to syringmyeliathough its one of the cause of itother causes include traumatumoranterior spinal cord ischemia Harrison pg no2440 Resyringomyelia central cord syndrome.
When cervical spinal cord is involved the patients may present with upper motor neuron weakness with preferential involvement of upper extremities man-in-the-barrel syndrome bladder dysfunction and variable sensory loss.
Injury to the central region of the spinal cord central corticospinal tracts and decussating fibers of the lateral spinothalamic tract Epidemiology. Syringomyelia can be classified into two types. Pain and temperature sensory deficits occur early but may not be recognized for years. Central Cord Syndrome Central cord syndrome may be caused by syringomyelia or intramedullary cord tumors. Clinical features Often asymptomatic andor slowly progressing similar to central cord syndrome. Some physicians use the terms syringomyelia or hydromyelia interchangeably. When cervical spinal cord is involved the patients may present with upper motor neuron weakness with preferential involvement of upper extremities man-in-the-barrel syndrome bladder dysfunction and variable sensory loss. Central cord syndrome can often be missed in the ED as the imaging in these patients is often unremarkable and their sensory deficits can be patchy. The latter category includes those caused by 1 contusion 2 compression 3 traction 4 arachnoiditis 5 tumors and 6 ischemia.
Communicating syringomyelia is a primary dilatation of the central canal and noncommunicating syringomyelia is a cyst arising in the cord parenchyma and does not communicate with the central canal or subarachnoid space. The latter category includes those caused by 1 contusion 2 compression 3 traction 4 arachnoiditis 5 tumors and 6 ischemia. Most common location is lower cervical upper thorasic cord. The signs and symptoms of lumbosacral syringomyelia are similar to those of tethered cord syndrome TCS caused by the lesion being in the central portion of the spinal cord. What are symptoms of syringomyelia. Some individuals have a condition related to syringomyelia known as hydrosyringomyelia which is characterized by abnormal widening of the central canal of the spinal cord the normal small canal running through the center of the spinal cord. Syringomyelia is an abnormal fluid-filled dilation of the central canal of the spinal cord occurring as a result of impaired CSF flow.




























Posting Komentar untuk "Syringomyelia Vs Central Cord Syndrome"