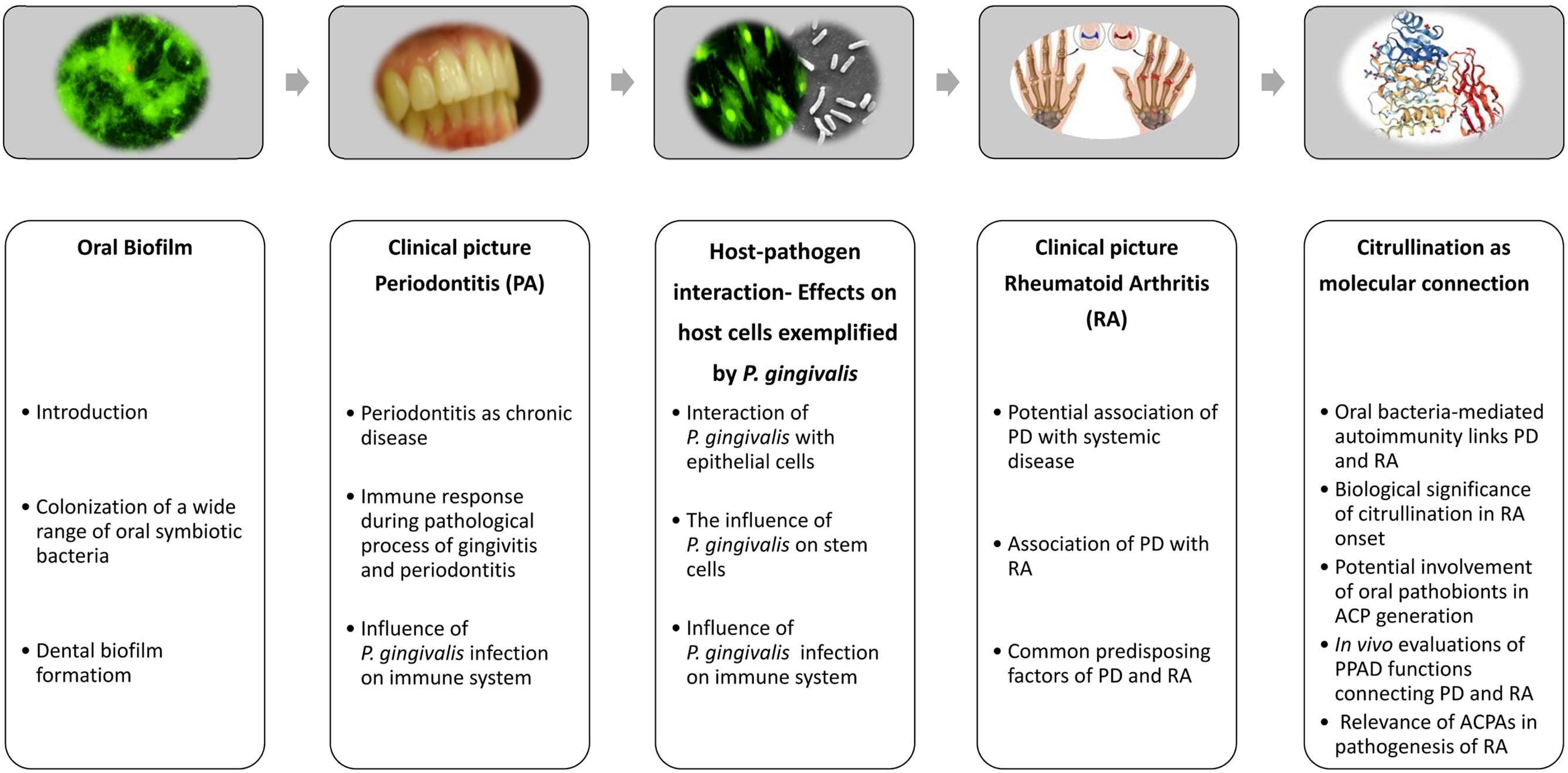
Bacteria Involved In Periodontal Disease
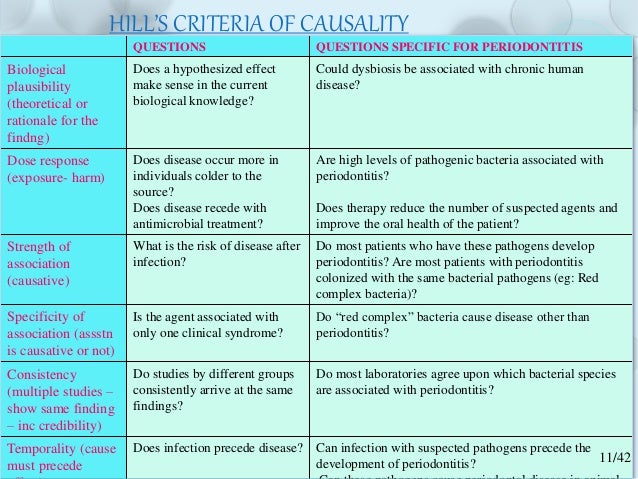
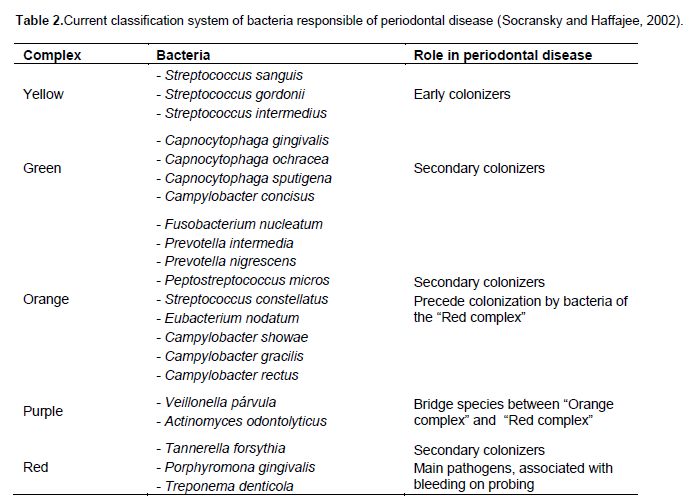
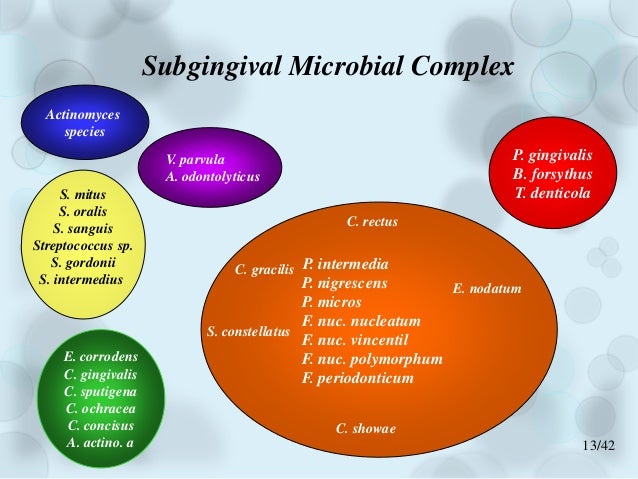
Bacteria involved in periodontal disease. Current classification system of bacteria responsible of periodontal disease Socransky and Haffajee 2002. These two bacteria appear to be particularly likely to cause aggressive periodontal disease. Recently attention has been focused on the relationship between the periodontopathic bacterium Porphylomonas gingivalis and AD.
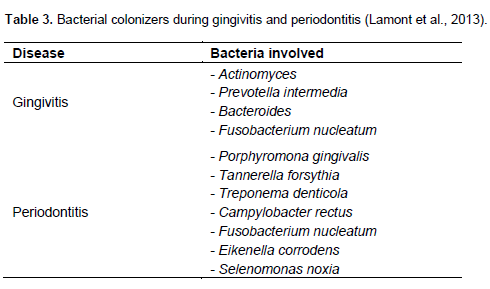
54 In addition to these bacteria it is thought that several periodontal pathogens such as Porphyromonas gingivalis Prevotella intermedia Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Because there is a complex microbiota involved in the formation of plaque biofilm first we need to distinguish the pathogenic bacterial. Periodontal disease can be initiated in gnotobiotic germ-free animals by specific periodontopathic bacteria isolated from human dental plaque eg.
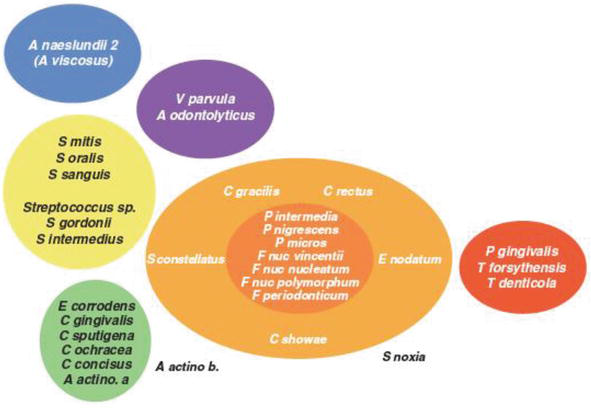
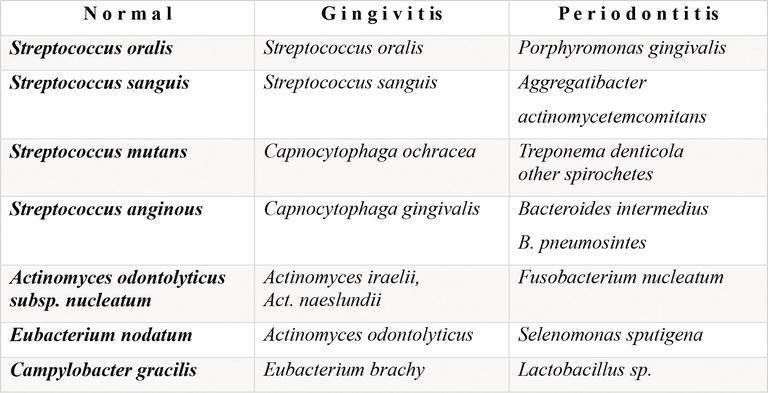
Complex Bacteria Role in periodontal disease Yellow - Streptococcus sanguis - Streptococcus gordonii - Streptococcus intermedius Early colonizers Green - Capnocytophaga gingivalis - Capnocytophaga ochracea - Capnocytophaga sputigena. In periodontal disease the bacterial balance shifts over to gram negative. Various bacterial species have been reported to be related to periodontitis among which we recently focused on 10 species including Porphyromonas gingivalis Pg Tannerella forsythia formerly Tannerella forsythensis Tf Prevotella intermedia Pi Prevotella.
Forsynthus an anaerobic Gram-negative bacterial species. Intermedius and Treponema sp. Bacterial species other than the classical periodontal pathogens may be involved in periodontal diseases since the classical putative periodontal pathogens Treponema denticola Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia may be below the limit of detection.
Most implicated bacteria include. It has been implicated in periodontal diseases and is a member of the red complex of periodontal pathogens. The bacteria associated with periodontal diseases are predominantly gram-negative anaerobic bacteria and may include A.
Periodontal disease in HIV. Identification of Bacteria Involved in Periodontal Disease Using Molecular Biology Techniques IOANA MARTU 1 ANCUTA GORIUC 2 MARIA ALEXANDRA MARTU IOANAVATA 3 RALUCA BACIU 1 RALUCA MOCANU 4. On the other hand it is thought that Aβ-containing microorganisms are deposited in brain tissue resulting in the formation of senile plaques that cause damage to cranial nerves and exacerbate the condition of AD.
On the other hand it has been pointed out that chronic inflammation and microbial infection in the brain may be involved in the pathogenesis of AD. Fusobacterium nucleatum Porphyromonas gingivalis and the disease can be arrested by administering antibiotics active against that particular organism.
54 In addition to these bacteria it is thought that several periodontal pathogens such as Porphyromonas gingivalis Prevotella intermedia Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.
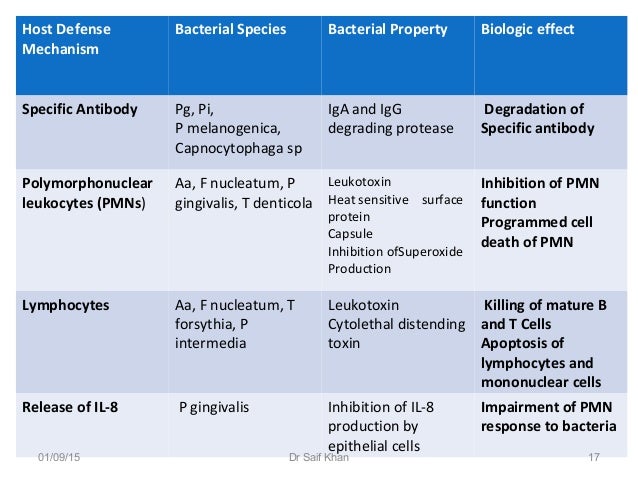
Collagenase Mechanism of virulence Collagenases are zinc endopeptidasesextracellular proteolytic enzymes secreted by bacteria that digest nearly all collagen fibers in their insoluble triple helical form. Most implicated bacteria include. The bacteria associated with periodontal diseases are predominantly gram-negative anaerobic bacteria and may include A. Because there is a complex microbiota involved in the formation of plaque biofilm first we need to distinguish the pathogenic bacterial. Collagenase Mechanism of virulence Collagenases are zinc endopeptidasesextracellular proteolytic enzymes secreted by bacteria that digest nearly all collagen fibers in their insoluble triple helical form. In periodontal disease the bacterial balance shifts over to gram negative. Bacterial species in the periodontal environment that are part of the commensal flora Actinomyces certain Streptococcus and Staphylococcus spp can provoke opportunistic infections. 5 linhas The species present include key periodontal pathogens such as Aggregatibacter. Fusobacterium nucleatum Porphyromonas gingivalis and the disease can be arrested by administering antibiotics active against that particular organism.
These two bacteria appear to be particularly likely to cause aggressive periodontal disease. 5 linhas The species present include key periodontal pathogens such as Aggregatibacter. Recently attention has been focused on the relationship between the periodontopathic bacterium Porphylomonas gingivalis and AD. Complex Bacteria Role in periodontal disease Yellow - Streptococcus sanguis - Streptococcus gordonii - Streptococcus intermedius Early colonizers Green - Capnocytophaga gingivalis - Capnocytophaga ochracea - Capnocytophaga sputigena. Periodontal diseases are caused by a variety of micro-organisms that reside at or below the gingival margin in the form of plaque biofilm. Because there is a complex microbiota involved in the formation of plaque biofilm first we need to distinguish the pathogenic bacterial. On the other hand it is thought that Aβ-containing microorganisms are deposited in brain tissue resulting in the formation of senile plaques that cause damage to cranial nerves and exacerbate the condition of AD.























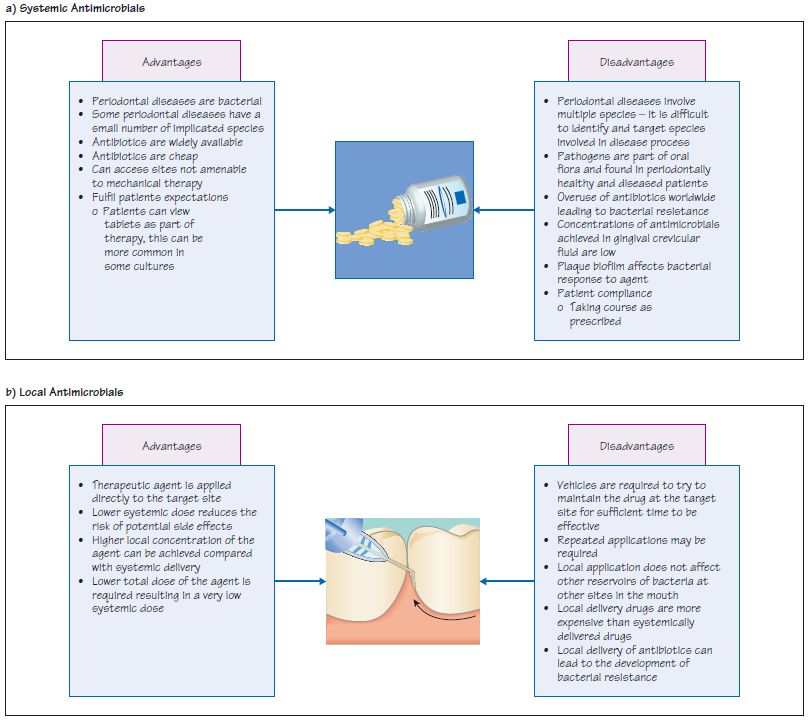

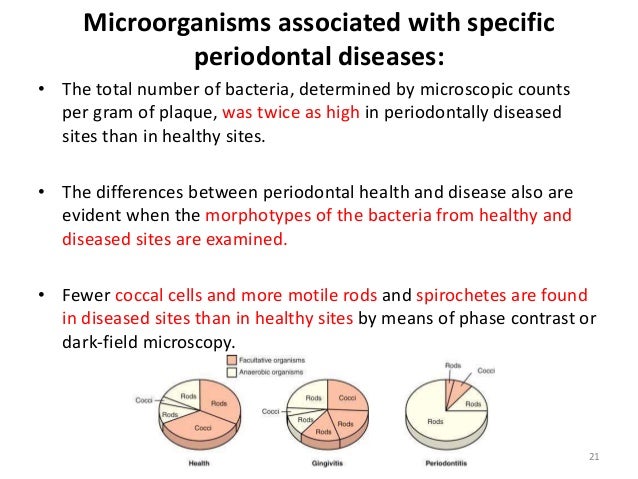




Posting Komentar untuk "Bacteria Involved In Periodontal Disease"