Multiple Myeloma Bone Disease
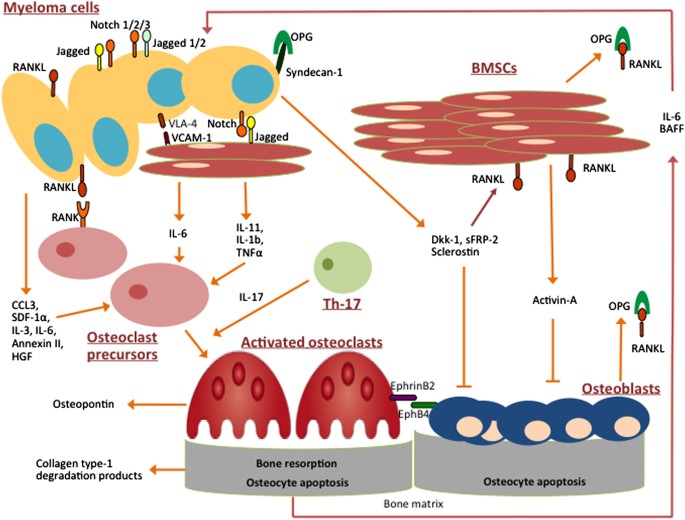
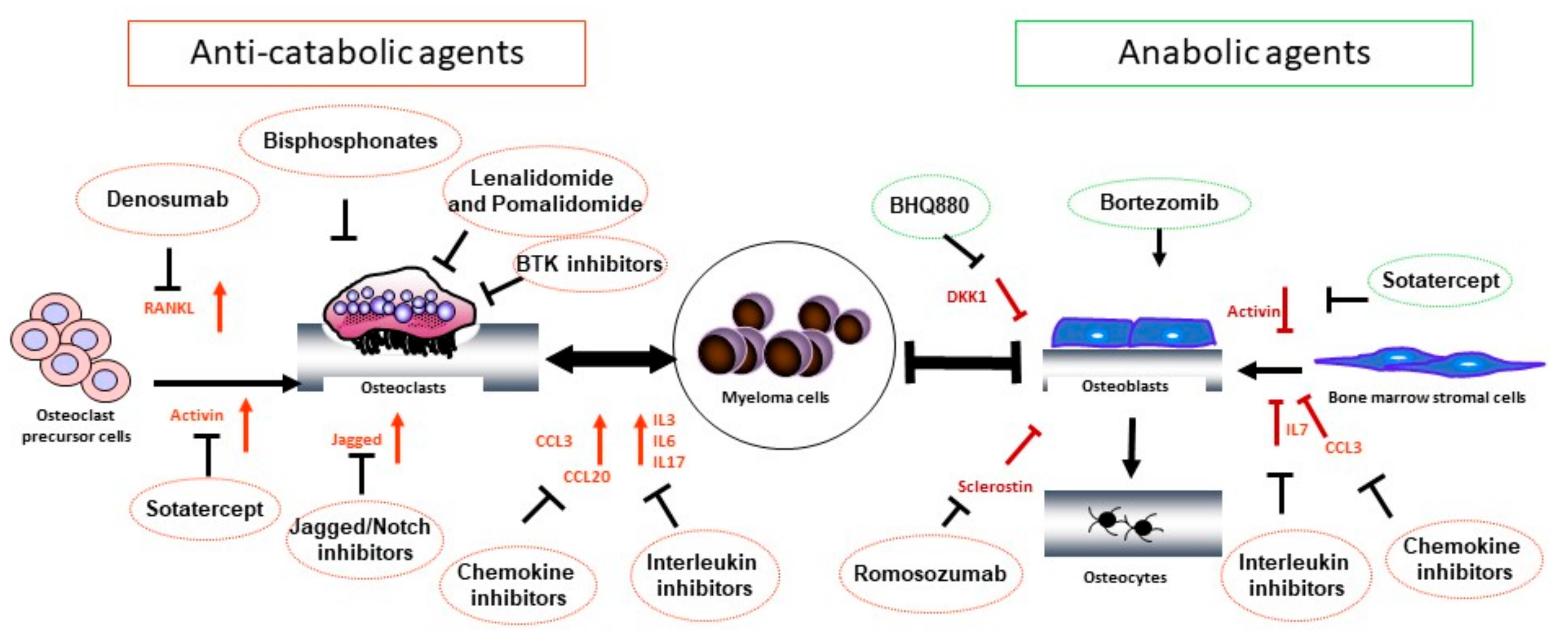
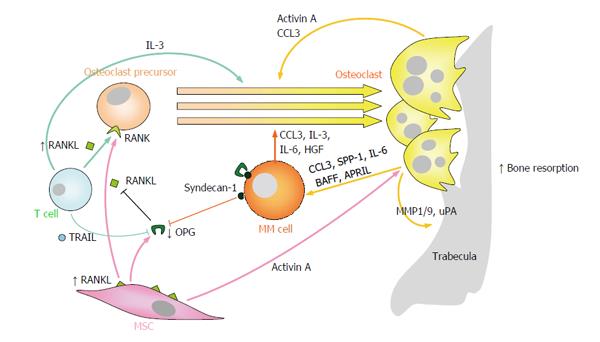
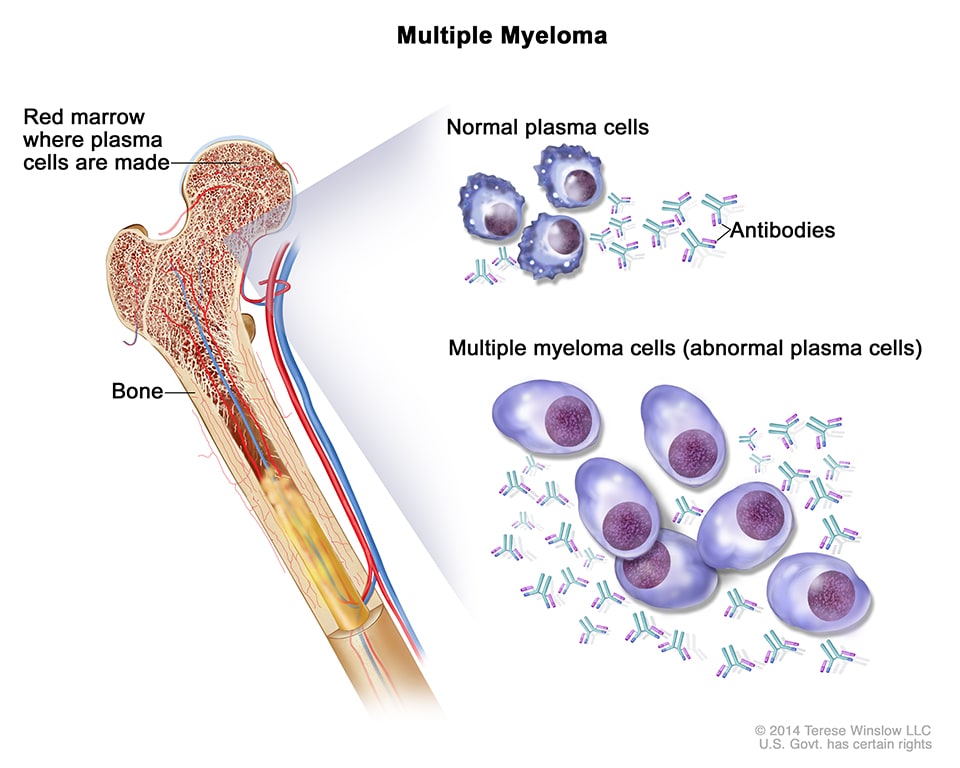
Multiple myeloma bone disease. Bone destruction in MM results from increased osteoclast formation and activity that occur in close proximity to myeloma cells. Bone destruction in MM results from increased osteoclast formation and activity that occur in close proximity to myeloma cells. Bone disease is a key feature of multiple myeloma.
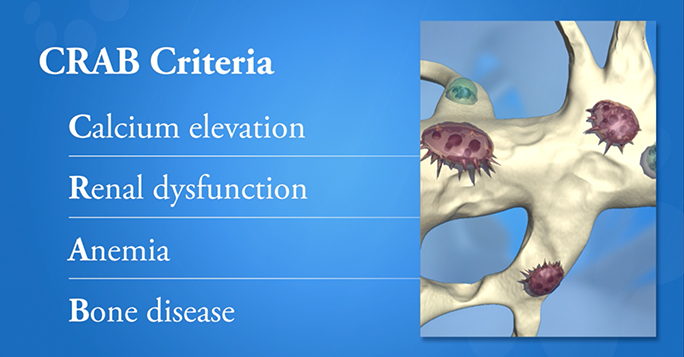
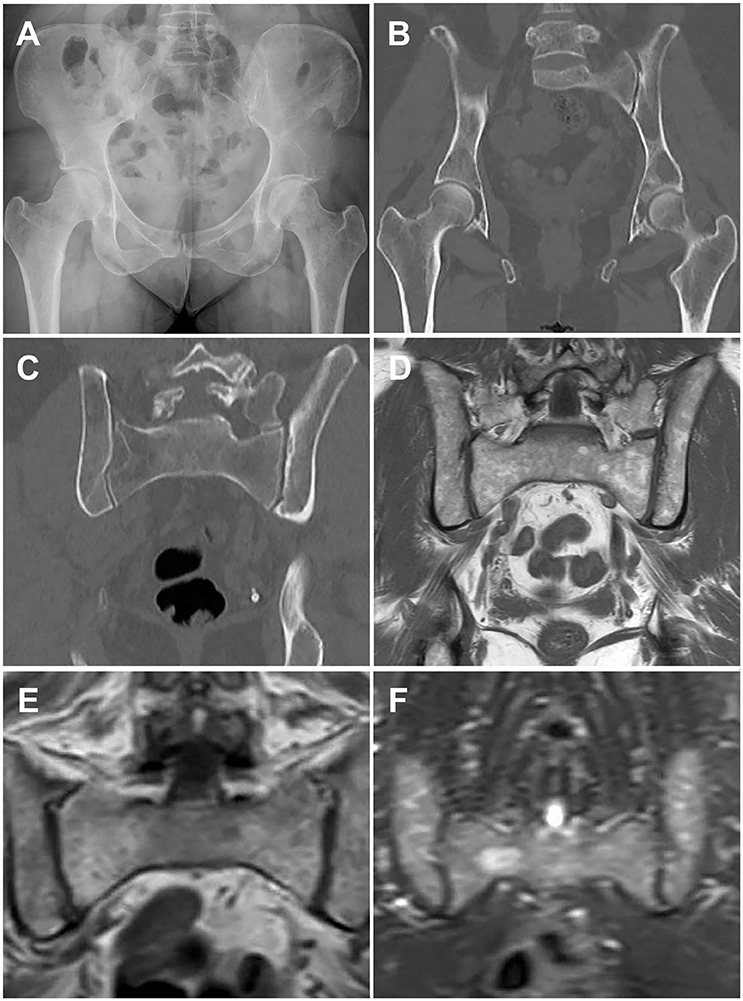
52-55 Bone disease is characterized by lytic lesions commonly found in the vertebrae ribs skull shoulders pelvis and long bones. It is also a major cause of morbidity and mortality in these patients. The bone disease can lead to pathologic fractures spinal cord compression hypercalcemia and pain.
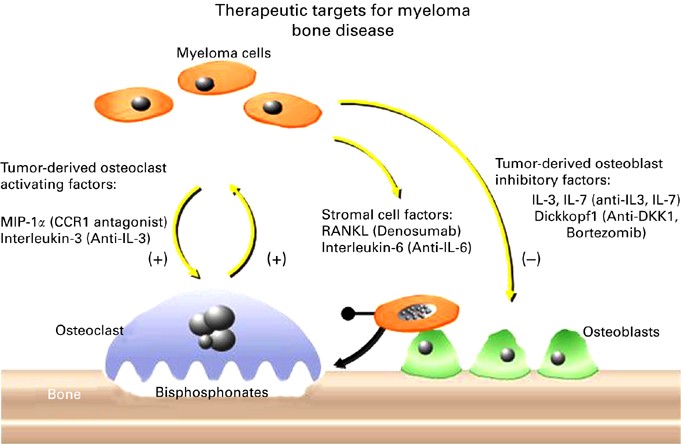
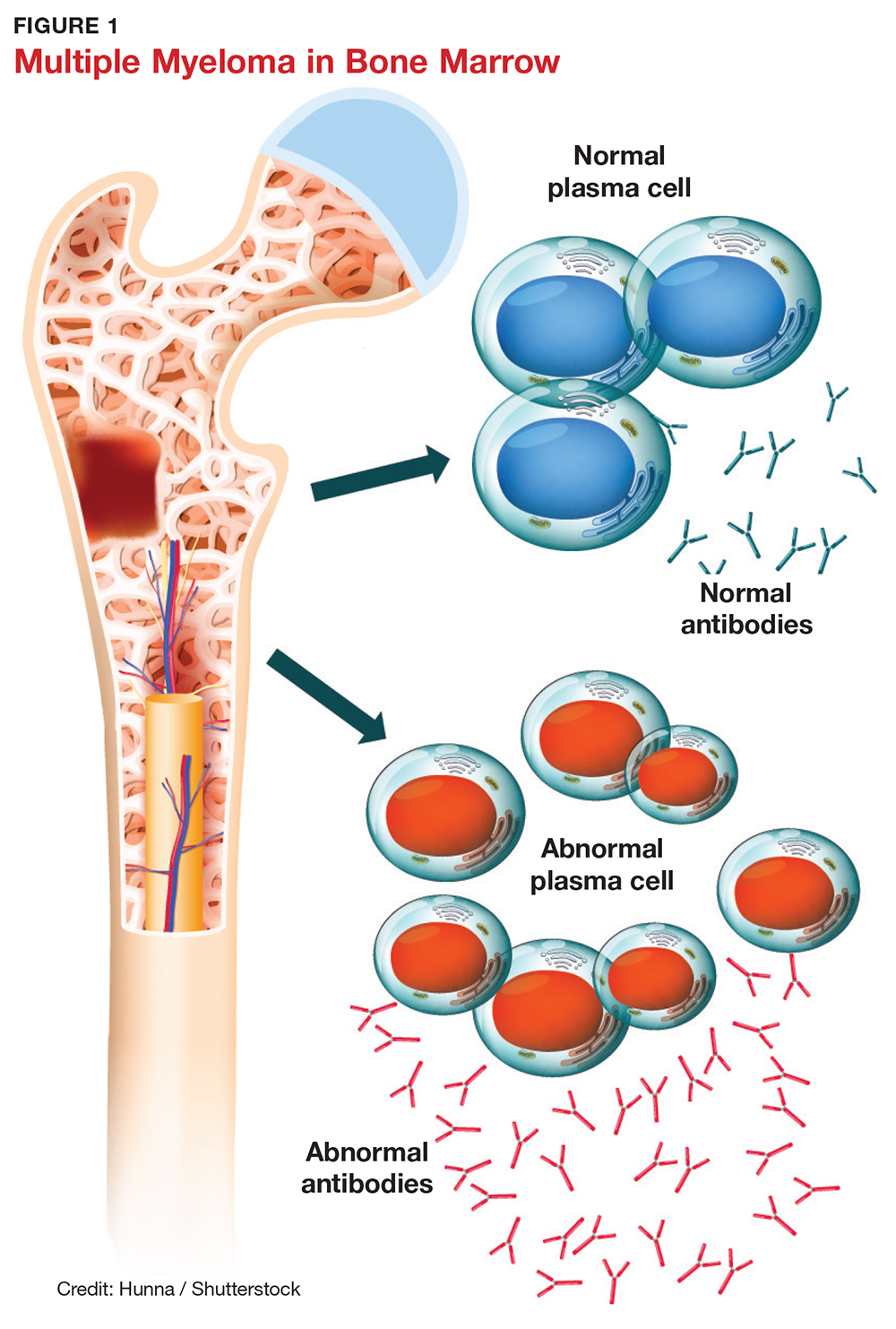
Multiple myeloma-A painful disease of the bone marrow. Currently bisphosphonates BPs are the mainstay for the treatment of myeloma bone disease. Multiple myeloma MM is a plasma cell malignancy characterized by a high capacity to induce osteolytic bone lesions.
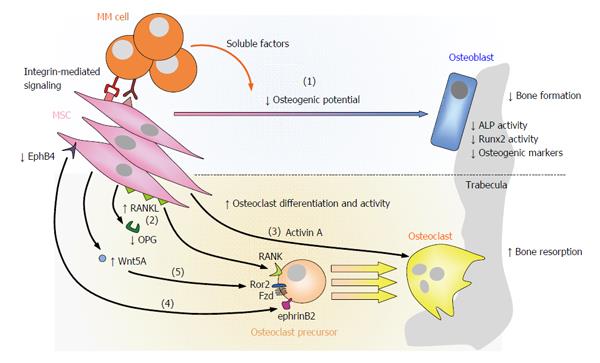
The major clinical manifestation of multiple myeloma is related to the osteolytic bone destruction. Osteocytes produce molecules that regulate both bone formation and resorption. Progression of multiple myeloma MM is largely dependent on the bone marrow BM microenvironment wherein communication through different factors including extracellular vesicles takes place.
Osteolytic bone disease is the hallmark of multiple myeloma which deteriorates the quality of life of myeloma patients and it affects dramatically their morbidity and mortality. Multiple myeloma MM is a plasma cell malignancy characterized by a high capacity to induce osteolytic bone lesions. Zoledronic acid which has been found to be superior to clodronate both in terms of reduction of.
The Nordic myeloma study group compared the effect of. 1 These patients present with substantial bone pain and they are at high risk for developing skeletal-related events SREs such as pathological fractures spinal cord compression and need for radiotherapeutic or surgical intervention. 54 Bone disease can.
This cross-talk not only leads to drug resistance but also to the development of osteolysis. Bone disease affects up to 80 of the newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma NDMM.
Multiple myeloma reduces vertebral fracture probably pain and possibly the incidence of hypercalcaemia.
Currently bisphosphonates BPs are the mainstay for the treatment of myeloma bone disease. Bone destruction in MM results from increased osteoclast formation and activity that occur in close proximity to myeloma cells. Skeletal-related complications affect nearly all patients with multiple myeloma and have a major impact on both patient morbidity and mortality. Multiple myeloma-A painful disease of the bone marrow. 52-55 Bone disease is characterized by lytic lesions commonly found in the vertebrae ribs skull shoulders pelvis and long bones. Currently bisphosphonates BPs are the mainstay for the treatment of myeloma bone disease. Zoledronic acid which has been found to be superior to clodronate both in terms of reduction of. This cross-talk not only leads to drug resistance but also to the development of osteolysis. Bone destruction in MM results from increased osteoclast formation and activity that occur in close proximity to myeloma cells.
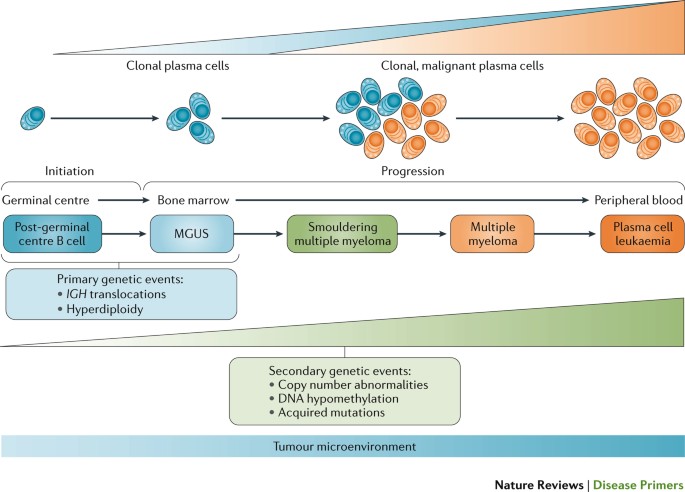
Progression of multiple myeloma MM is largely dependent on the bone marrow BM microenvironment wherein communication through different factors including extracellular vesicles takes place. The bone disease can lead to pathologic fractures spinal cord compression hypercalcemia and pain. It manifests as lytic lesions or osteopenia and is often associated with severe pain pathological fracture spinal cord compression vertebral collapse and hypercalcemia. Multiple myeloma MM is a plasma cell malignancy characterized by a high capacity to induce osteolytic bone lesions. Zoledronic acid which has been found to be superior to clodronate both in terms of reduction of. Multiple myeloma is a bone marrow neoplasia with an incidence of 6100000year in Europe. What is multiple myeloma.



































Posting Komentar untuk "Multiple Myeloma Bone Disease"