Kidney Disease And Magnesium
Kidney disease and magnesium. Low serum magnesium levels are associated with an elevated the risk of developing kidney disease according to a new study. Magnesium Intake and Impaired Kidney Function If your kidney function is impaired as is the case in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease your body may. Accumulation of magnesium in the blood can cause muscle weakness but does not damage the kidney directly.
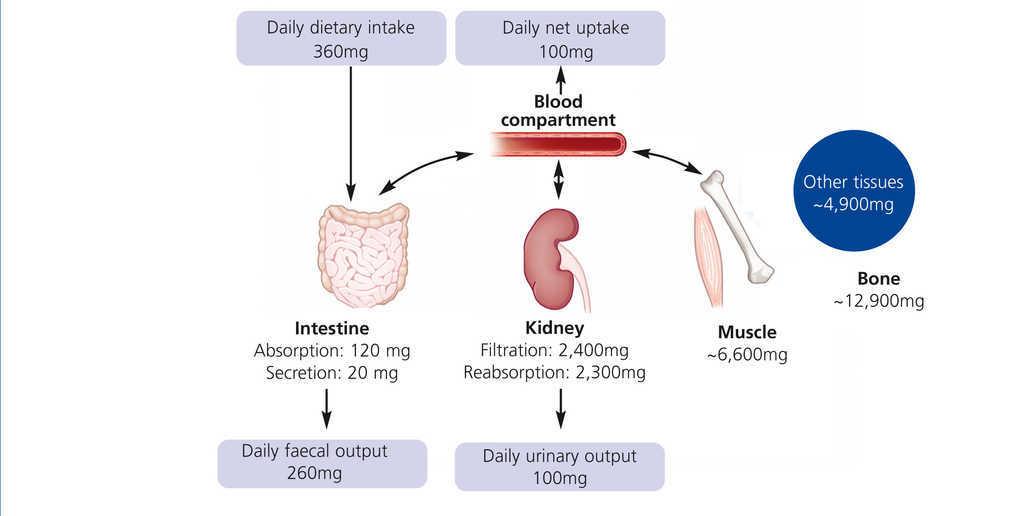
The kidneys are the main determinants of magnesium metabolism modulating along with the alimentary ingestion and the intestinal absorption the total body magnesium burden as well as its serum levels in humans both in healthy people and in patients with renal disease. Magnesium plays so many important roles within the body and not getting enough magnesium is linked to a variety of different symptoms and conditions. Magnesium supplements can cause excessive accumulation of magnesium in the blood especially with patients who have chronic kidney disease.
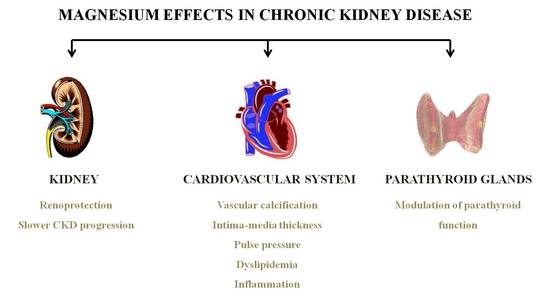
The kidney plays a major role in regulating the Mg balance. Magnesium supplements also increase your chances of slowing down the progression of the deadly kidney disease. These numbers vary from time to time and you may check the ranges frequently.
Magnesium is a biological necessity and the blanket avoidance of it in kidney disease has led to untold suffering. In moderate chronic kidney disease CKD increases in the fractional excretion of magnesium largely compensate for the loss of glomerular filtration rate to maintain normal serum magnesium levels. Thats because when you are not able to urinate your kidneys can no longer eliminate excess minerals like magnesium which can build up in your body.
Magnesium plays a critical role in cellular physiology in humans regulating many fundamental functions. In case of chronic kidney disease CKD renal regulatory. Magnesium levels and lower dietary magnesium intake are associated with an increased risk of incident CKD and progression to end-stage kidney disease.
I would ask this question of your physician. In a healthy individual total-body Mg content is kept constant by interactions among intestine bones and the kidneys. T2DM is often associated with hypomagnesaemia 17 and incidence rates of 135477 have been reported 18.
Studies show that magnesium deficiency in people with CKD is associated with a more. Because these associations are independent of traditional risk factors other pathways might be involved in the relationship between magnesium deficiency and the risk of CKD progression.
Diabetes damages the kidneys and is the leading cause of kidney disease.
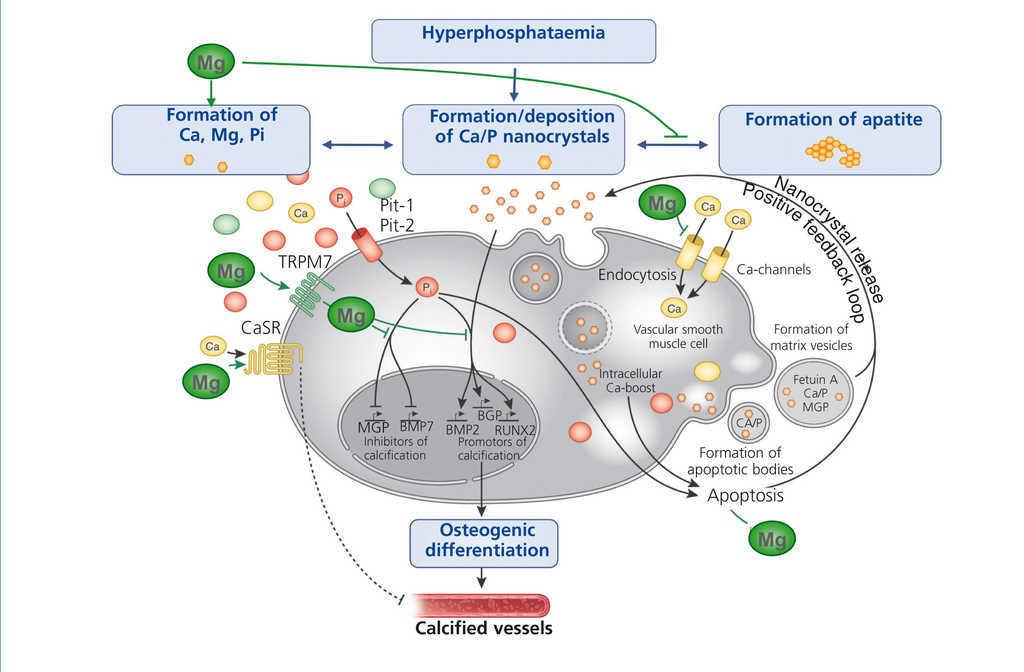
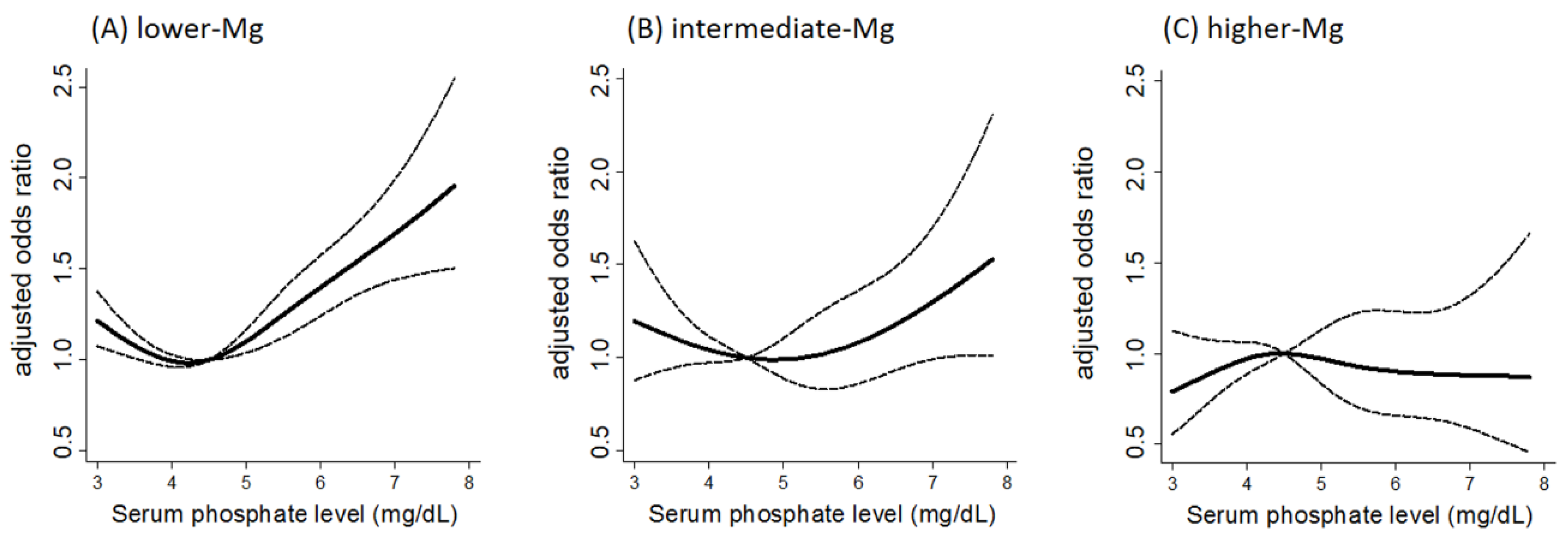
Hypomagnesaemia can be defined as serum magnesium concentrations 065 mmolL 16 mgdL or 2 SD below the average in the general population 19 20. The role of Magnesium in Kidney Disease. These numbers vary from time to time and you may check the ranges frequently. In case of chronic kidney disease CKD renal regulatory. Magnesium impairs the crystallization of calcium phosphatemore specifically the maturation of calciprotein particles. Magnesium supplements also increase your chances of slowing down the progression of the deadly kidney disease. Even alternative medicine practitioners parrot the safety warning that people with kidney disease should not take magnesium. Magnesium modifies the association between serum phosphate and the risk of progression to end-stage kidney disease in patients with non-diabetic chronic kidney disease. The kidney plays a major role in regulating the Mg balance.
One of the contraindications for taking magnesium is kidney failure which means the patient is on kidney dialysis. Magnesium supplements also increase your chances of slowing down the progression of the deadly kidney disease. Magnesium supplements can cause excessive accumulation of magnesium in the blood especially with patients who have chronic kidney disease. Thats because when you are not able to urinate your kidneys can no longer eliminate excess minerals like magnesium which can build up in your body. Having an adequate intake of magnesium is equally important for people with kidney disease. The kidneys are the main determinants of magnesium metabolism modulating along with the alimentary ingestion and the intestinal absorption the total body magnesium burden as well as its serum levels in humans both in healthy people and in patients with renal disease. Low serum magnesium levels are associated with an elevated the risk of developing kidney disease according to a new study.


































Posting Komentar untuk "Kidney Disease And Magnesium"